[ad_1]
Navigating Risky Markets
Monetary market merchants typically embrace volatility as a result of it presents alternatives for vital earnings, albeit with larger dangers. Volatility refers back to the diploma of variation within the value of a monetary instrument over time. When markets are risky, prices fluctuate quickly, creating potential for merchants to capitalize on short-term value actions. This is a more in-depth have a look at why merchants like volatility and the way they observe and commerce it:
Revenue potential: Risky markets might supply merchants the prospect to make earnings in a short while. Speedy value swings permit merchants to purchase low and promote excessive inside a compressed timeframe, amplifying potential returns. The bigger the worth actions, the higher the potential for merchants who can precisely predict market route.
Elevated buying and selling alternatives: Volatility creates extra buying and selling alternatives as costs transfer extra often and with higher magnitude. Merchants can make the most of these value swings by using numerous methods, akin to scalping, day buying and selling, or swing buying and selling. Extra volatility means extra probabilities to enter and exit positions, probably growing the variety of worthwhile trades.
Grasp the Three Most Essential Market Circumstances with our Complimentary Guides
Recommended by Nick Cawley
Recommended by Nick Cawley
Master The Three Market Conditions
Enhanced liquidity: Risky markets typically entice extra market individuals, together with merchants and buyers. Elevated participation results in larger volumes and improved liquidity. With extra patrons and sellers out there, merchants can execute their trades extra simply and with tighter spreads, lowering transaction prices.
To observe and commerce volatility, merchants can use a number of instruments and methods:
Volatility indicators: Merchants make use of technical indicators particularly designed to measure and observe volatility. Common indicators embrace the Average True Range (ATR), Bollinger Bands, and the Volatility Index (VIX). These indicators assist merchants gauge the extent of volatility out there and make knowledgeable buying and selling choices.
What is the VIX? A Guide to the S&P 500 Volatility Index
Using Average True Range (ATR) to Measure Volatility in Financial Markets
Chart patterns: Merchants analyze value charts to establish patterns that point out potential volatility. Sure chart patterns, akin to breakouts, development traces, and assist/resistance ranges, can sign impending volatility. By recognizing these patterns, merchants can put together for potential value actions and regulate their methods accordingly.
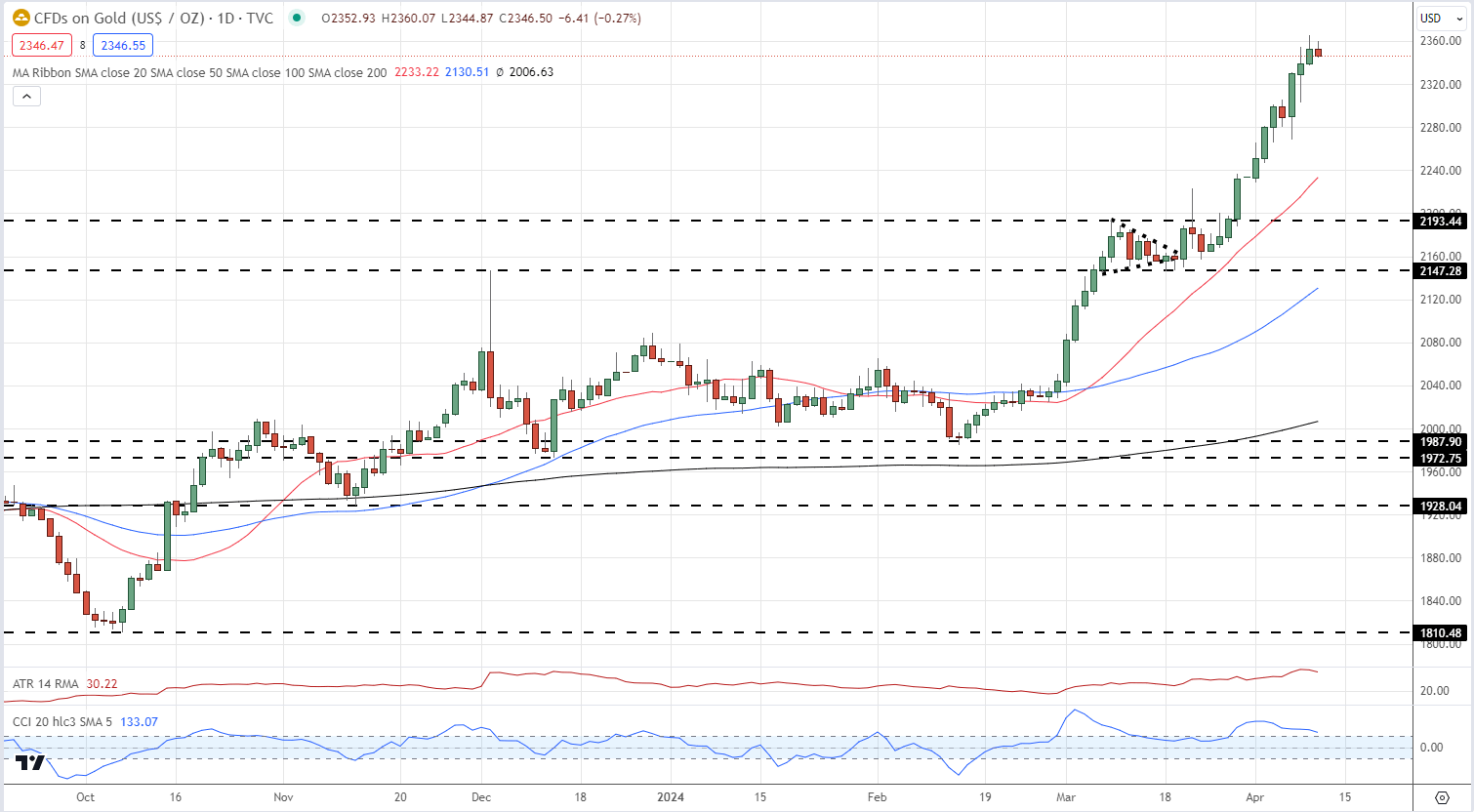
Gold Chart with Easy Transferring Averages, Help and Resistance Ranges, and ATR
Financial calendar: Merchants carefully monitor the financial calendar for high-impact occasions that may set off volatility. Occasions, akin to central financial institution conferences, curiosity rate decisions, GDP releases, and geopolitical developments can considerably influence monetary markets. Merchants typically place themselves forward of those occasions or react rapidly to the ensuing market strikes.
For all market-moving financial knowledge and occasions, use the DailyFX Economic Calendar
Threat administration: Whereas volatility presents alternatives, it additionally carries elevated threat. Merchants should make use of sturdy threat administration methods to navigate risky markets successfully. This consists of setting acceptable stop-loss orders, managing place sizes, and diversifying their buying and selling portfolio. Correct threat administration helps merchants shield their capital during times of heightened volatility.
Risk Management Techniques for Trading
Adaptive methods: Profitable merchants adapt their methods to altering market circumstances. They might make use of completely different buying and selling approaches relying on the extent of volatility. For instance, throughout excessive volatility, merchants would possibly concentrate on shorter-term trades and use wider stop-loss ranges. Conversely, throughout low volatility, they could pursue longer-term positions and make use of tighter threat controls.
In conclusion, by using volatility indicators, analyzing chart patterns, monitoring financial occasions, and using adaptive methods, merchants can navigate the challenges and alternatives offered by risky markets.
Recommended by Nick Cawley
Building Confidence in Trading
[ad_2]